Complies with 3% Inlet Pressure Drop Standard | Dual-Valve Backup Design
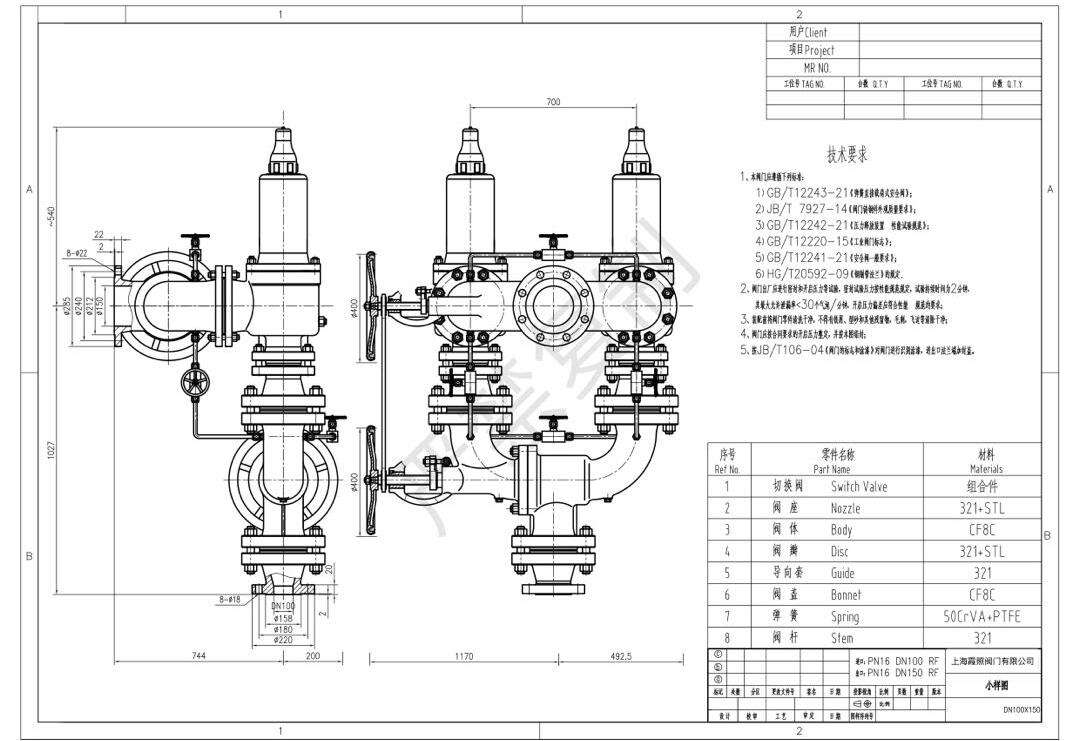
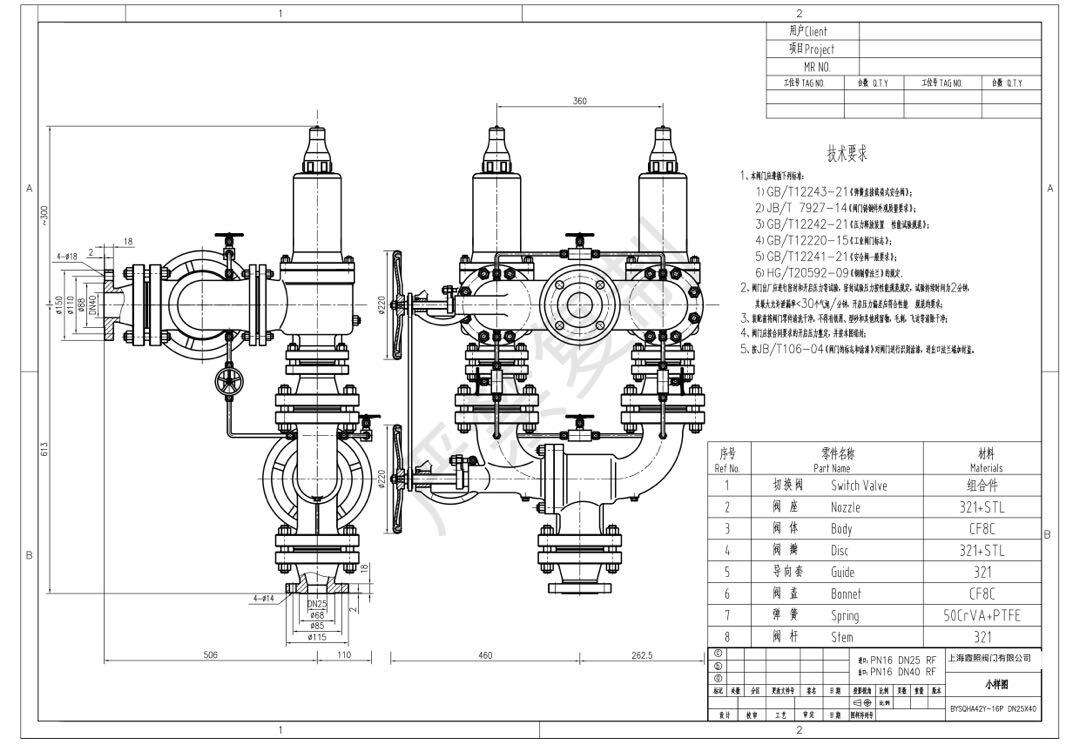
Technical data switching valve
Type: Single-switch valve & Dual-switch valve
Set pressure: 0.2 - 400 barg / 2 - 5802 psig
Connection method: DN2 to DN40
DIN EN 1952
Connection method: NPS 1" to NPS 16
ASME B16.5
BODY Material: WCB, LCB, LCC, LF2, CF8, CF8M
Support special materials


Simplified Calculation Template for Safety Valve Capacity and Throat Diameter
1. Basic Parameter Input Section (Fill in according to actual working conditions)
| Parameter Name | Symbol | Unit | Input Value | Remarks (Value Selection Instructions) |
| Medium Type | - | - | Optional: Gas/Liquid/Steam | |
| Vessel Operating Pressure | Pw | MPa | Design pressure of the vessel under normal operation | |
| Safety Valve Set Pressure | Po | MPa | Typically = 1.05~1.1 × Pw (per code requirements) | |
| Safety Valve Back Pressure | Pb | MPa | Pressure on the discharge side (fill in 0 if no back pressure) | |
| Medium Temperature | T | K | Absolute temperature (℃ + 273.15) | |
| Medium Density (for Liquid) | ρ | kg/m³ | Density of liquid at 20℃ (refer to medium property table) | |
| Medium Molar Mass (for Gas) | M | kg/kmol | Molecular weight of gas (e.g., air = 29, nitrogen = 28) | |
| Compressibility Factor (for Gas) | Z | - | Take 1 for ideal gas; check compressibility chart for high-pressure gas (usually 0.8~1.2) | |
| Safety Valve Flow Coefficient | K | - | Provided by valve manufacturer (if no data: 0.6~0.7 for standard valves, 0.8~0.9 for high-efficiency valves) |
2. Capacity Calculation Section (Select formula by medium type)
2.1 Liquid Medium Capacity Calculation
•Pressure Difference: ΔP = Po - Pb (MPa)
•Capacity Formula: Q_liquid = K × A × √(2×ΔP/ρ) (m³/h)
•Step-by-Step Calculation:
① ΔP = ______ (substitute Po and Pb values)
② √(2×ΔP/ρ) = ______
③ Temporarily assume A = 0.0001 m² (to be reversed later), Tentative Q_liquid = ______ m³/h
2.2 Gas Medium Capacity Calculation (Ideal Gas)
•Capacity Formula: Q_gas = K × A × Po × √(M/(T×Z)) × 3600 (m³/h)
•Step-by-Step Calculation:
① √(M/(T×Z)) = ______
② Po × √(M/(T×Z)) = ______
③ Temporarily assume A = 0.0001 m², Tentative Q_gas = ______ m³/h
2.3 Steam Medium Capacity Calculation (Simplified Formula)
•Capacity Formula: Q_steam = 0.5 × K × A × Po × 10⁶ / √T (kg/h)
•Step-by-Step Calculation:
① 10⁶ / √T = ______
② Po × 10⁶ / √T = ______
③ Temporarily assume A = 0.0001 m², Tentative Q_steam = ______ kg/h
3. Throat Diameter Calculation Section (Reverse minimum throat diameter from capacity)
| Step | Calculation Content | Formula | Calculation Result |
| 1 | Required Minimum Capacity (Actual Demand) | Q_required = ______ m³/h (liquid/gas) or kg/h (steam) | |
| 2 | Required Flow Area | A_required = Q_required / [“K×√(...)” term in the corresponding medium capacity formula] | A_required = ______ m² |
| 3 | Throat Diameter (Before Rounding) | d = √(4×A_required/π) | d = ______ mm |
| 4 | Standard Throat Diameter (After Rounding) | Select standard value ≥ d with reference to the table below | Final Throat Diameter = ______ mm |
4. Set Pressure Test Data Column (SEO Keywords: Safety Valve 3-Round Set Pressure Test, 1.9MPa Pressure Actual Measurement Data)
| Test Item | Test Pressure (MPa) | Pressure Holding Time (min) | Leakage (Bubbles/Minute) | Test Result | Remarks |
| Leak Test (Nitrogen) | 1.71 | 5 | 10 | Qualified | Back pressure during test: 0MPa |
| Air Tightness Test | 0.2 | 1 | No Leakage | Qualified | Test Medium: Nitrogen |
5. Sealing Performance Test Data Column (SEO Keywords: Safety Valve Bubble Leak Test, 1.71MPa Sealing Pressure Verification)
| Test Round | Required Set Pressure (MPa) | Actual Opening Pressure (MPa) | Pressure Deviation (%) | Adjustment Record (If Any) | Test Result |
| Round 1 | 1.9 | 1.91 | 0.50% | No Adjustment | Qualified |
| Round 2 | 1.9 | 1.91 | 0.50% | No Adjustment | Qualified |
| Round 3 | 1.9 | 1.91 | 0.50% | No Adjustment | Qualified |
| Average | 1.9 | 1.91 | 0.50% | Qualified |
6. Notes
1.After calculation, ensure: Flow area A of standard throat diameter ≥ Calculated A_required; otherwise, the capacity will be insufficient.
2.For real gas medium, correct the compressibility factor Z (cannot be ignored under high-pressure conditions).
3.For saturated steam, the simplified formula can be used directly; for superheated steam, multiply by a superheat correction factor (1.05~1.1).
4.If the flow coefficient K is not specified, consult the valve manufacturer first; use a conservative value (0.6) if no data is available to avoid undersizing.
