As a safety valve engineer with 20 years of experience, I'm delighted to share insights into safety valves. These valves are crucial in industrial systems, acting as the last line of defense to prevent equipment overpressure and ensure operational safety.
Safety valves find extensive application across numerous industries. In the petroleum industry, they safeguard oil pipelines, storage tanks, and refining equipment from overpressure during oil extraction, transportation, and processing. For instance, in an oil refinery's distillation column, a safety valve prevents damage if pressure spikes due to unexpected changes in feedstock or process conditions.
In the chemical sector, they protect reactors, chemical storage vessels, and pipelines handling corrosive or reactive chemicals. Take a chemical plant producing fertilizers; safety valves on ammonia synthesis reactors ensure pressure doesn't exceed safe limits, preventing hazardous reactions.
The power industry relies on them for boilers and steam turbines. In a coal-fired power plant, safety valves on the boiler drum release excess pressure if water level or firing rate goes awry, avoiding boiler explosions.
In pharmaceuticals, they're essential for sterilization equipment and pressure vessels used in drug manufacturing. During the production of injectable medications, autoclaves use safety valves to maintain safe pressure during sterilization cycles.
In essence, wherever fluids are stored or processed under pressure, safety valves are vital to prevent equipment failure, accidents, and ensure the smooth running of industrial operations. When the pressure in a system exceeds a preset value, a safety valve opens automatically to discharge fluid, reducing the pressure. Once the pressure drops to a safe level, it closes tightly to maintain system pressure.
Classification of Safety Valves
Safety valves can be classified based on the medium they handle and structural/operating principles, as shown in the diagram:
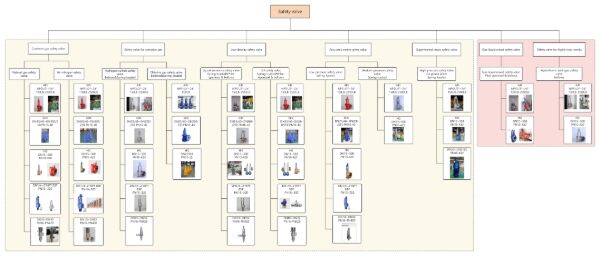
1. Common Gas Safety Valve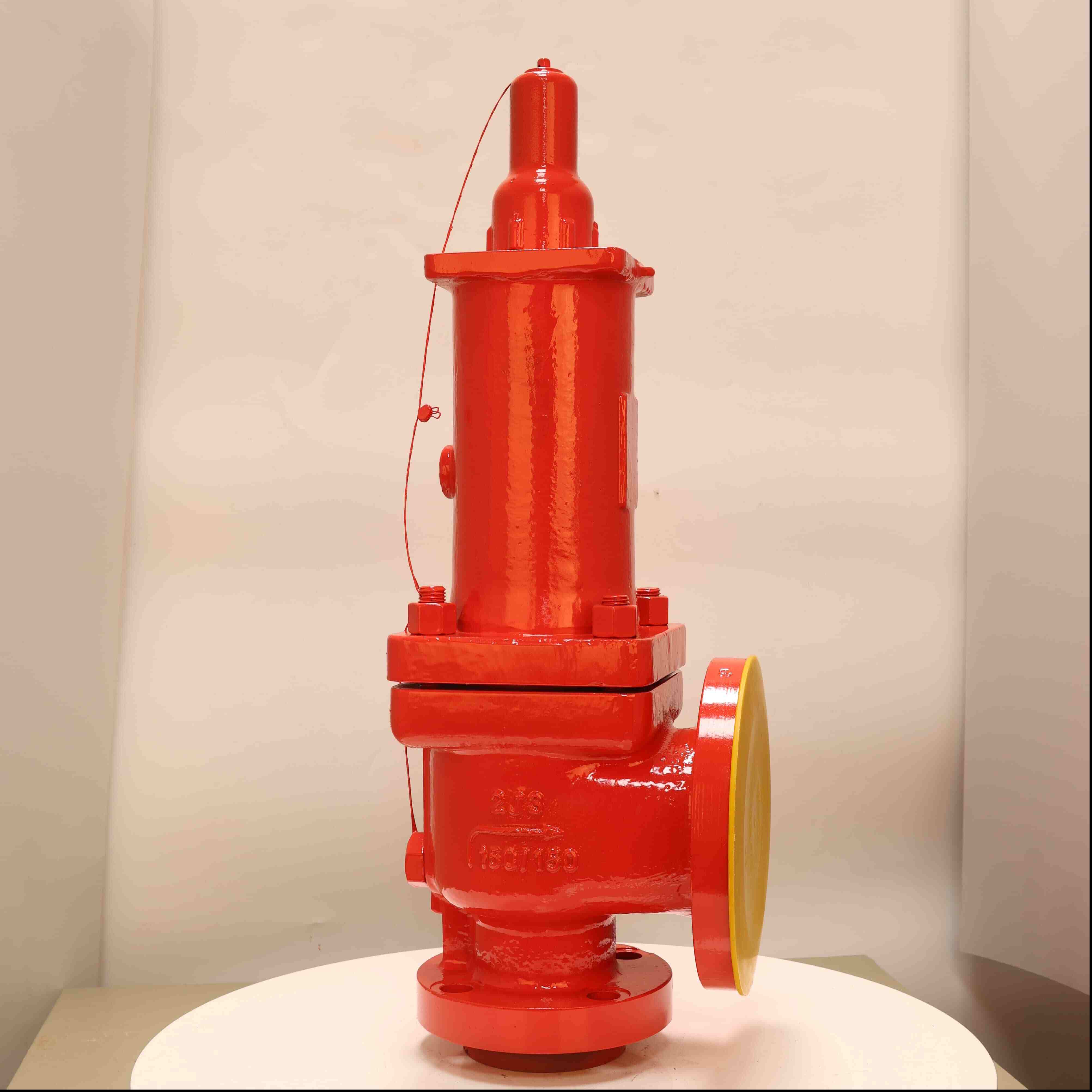
2.Safety Valve for Corrosive Gas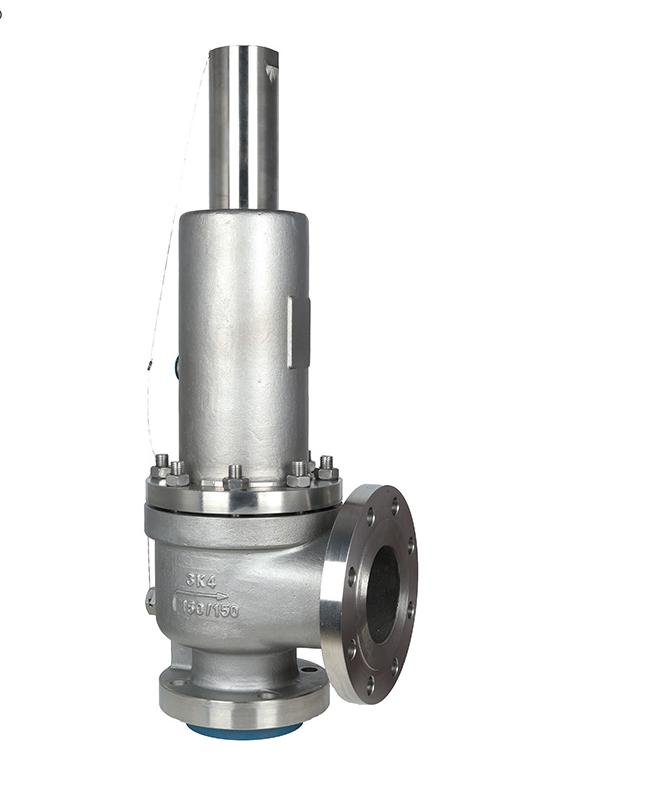
3.Low-density Safety Valve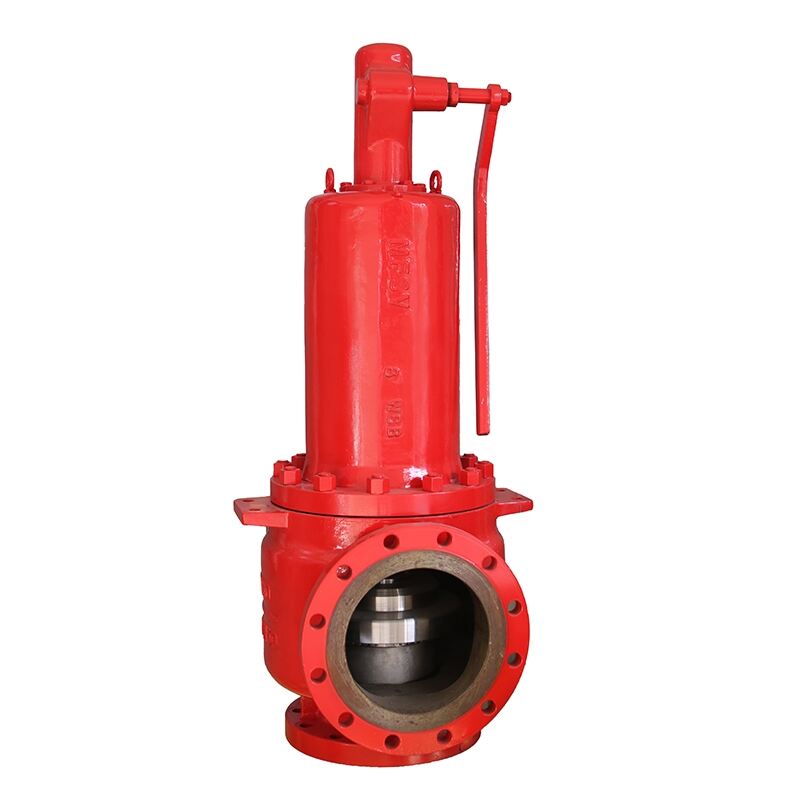
4.Saturated Steam Safety Valve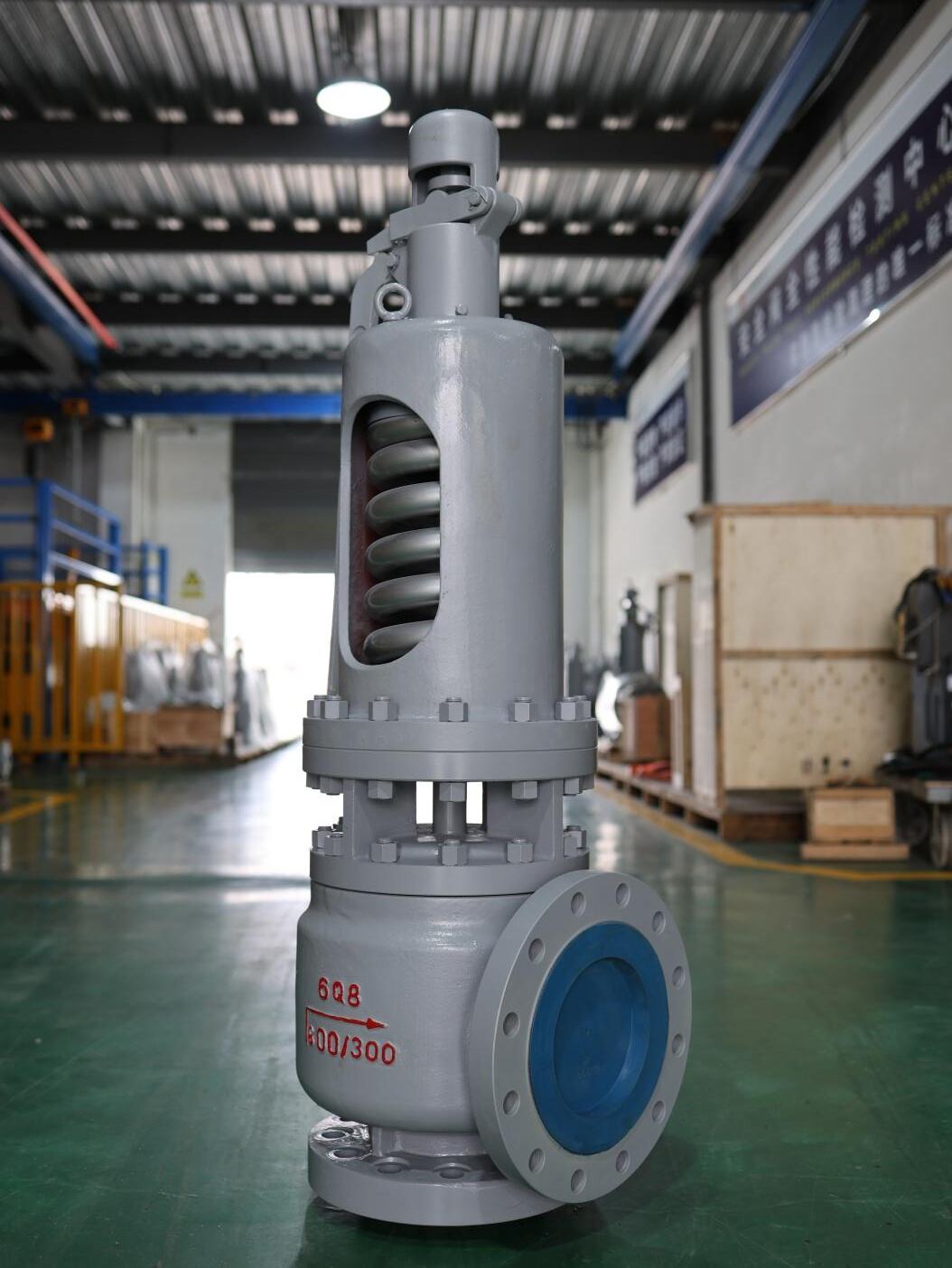
5. Superheated Steam Safety Valve
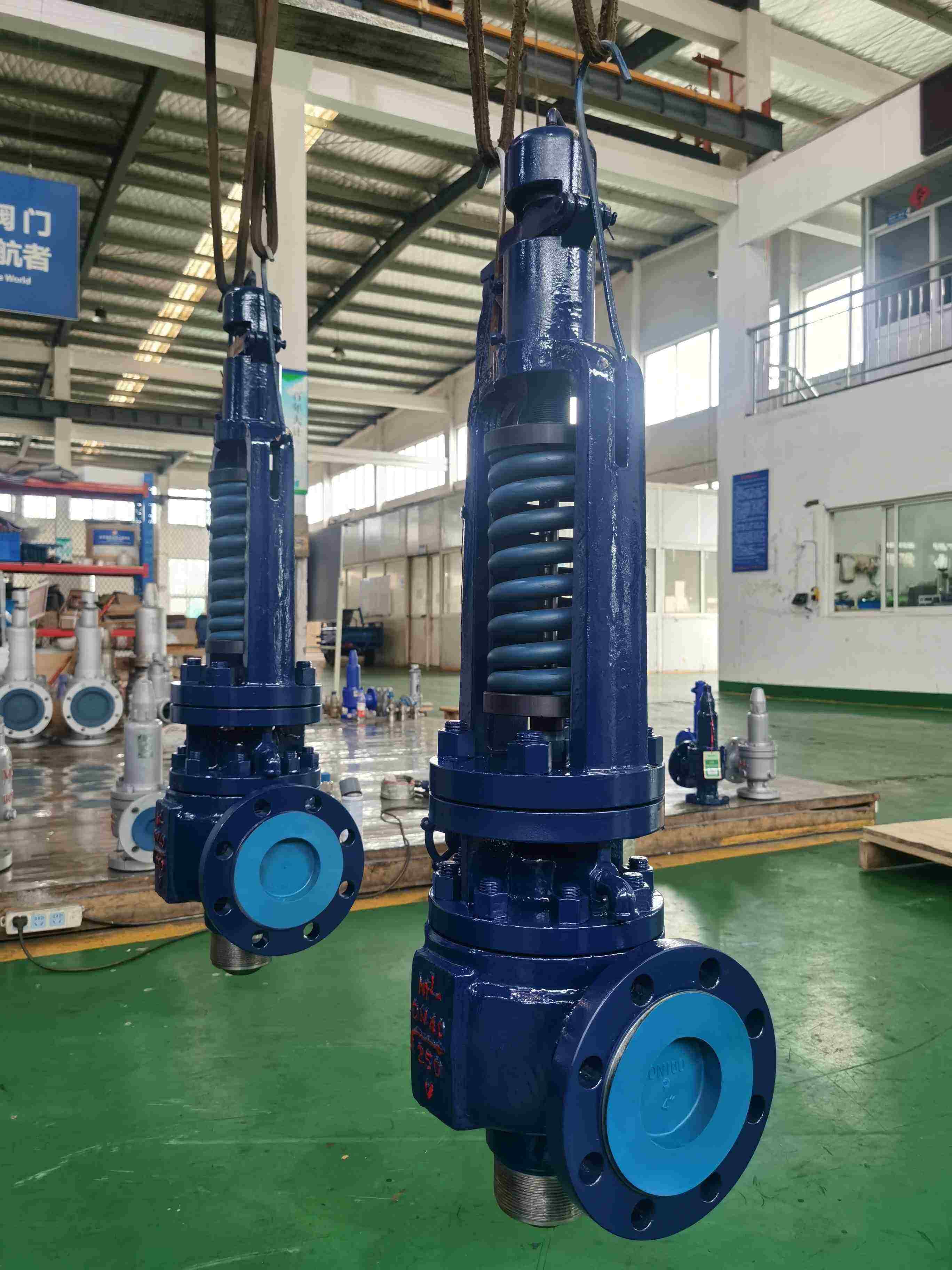
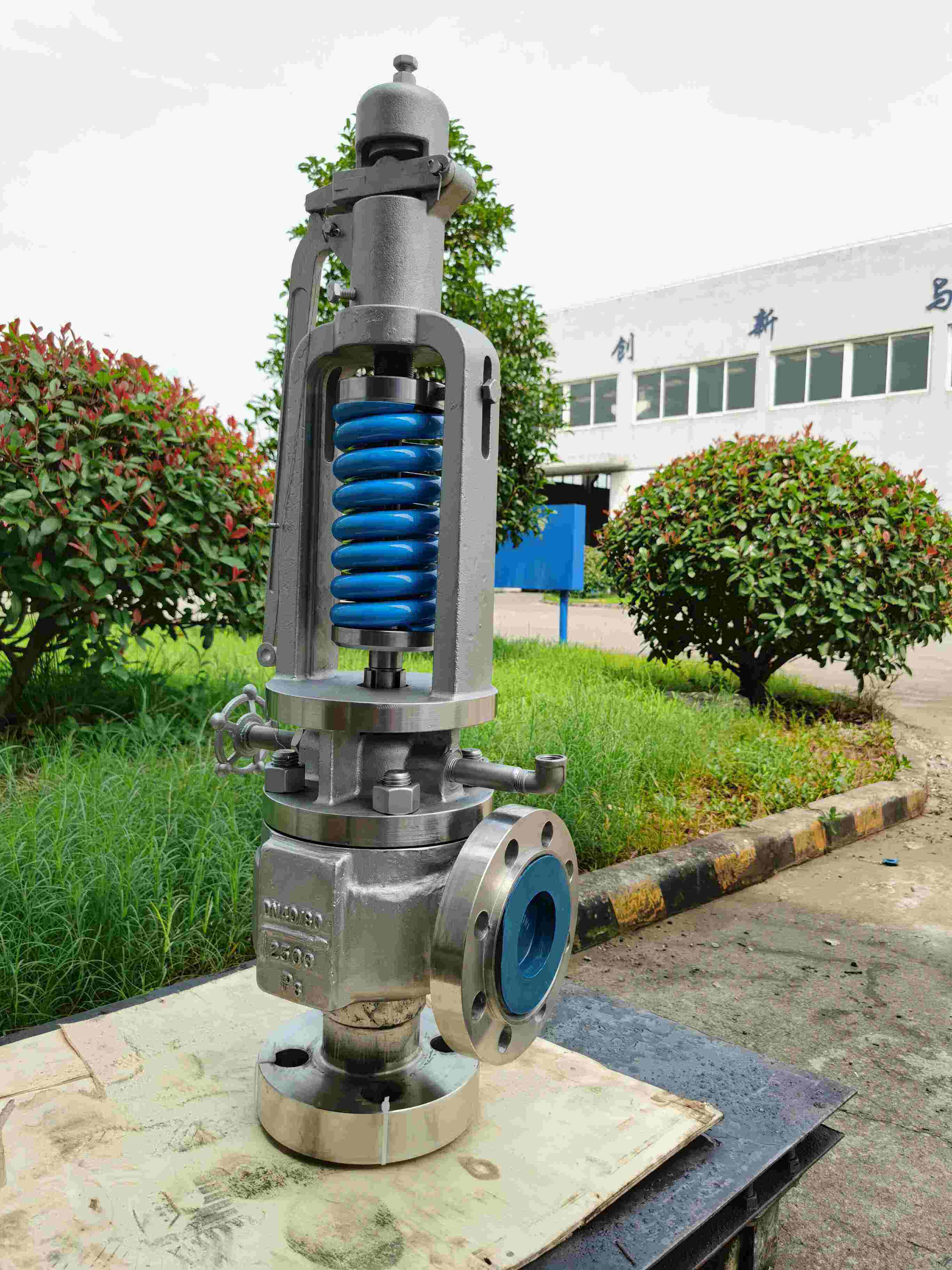


6. Gas-liquid Mixed Safety Valve
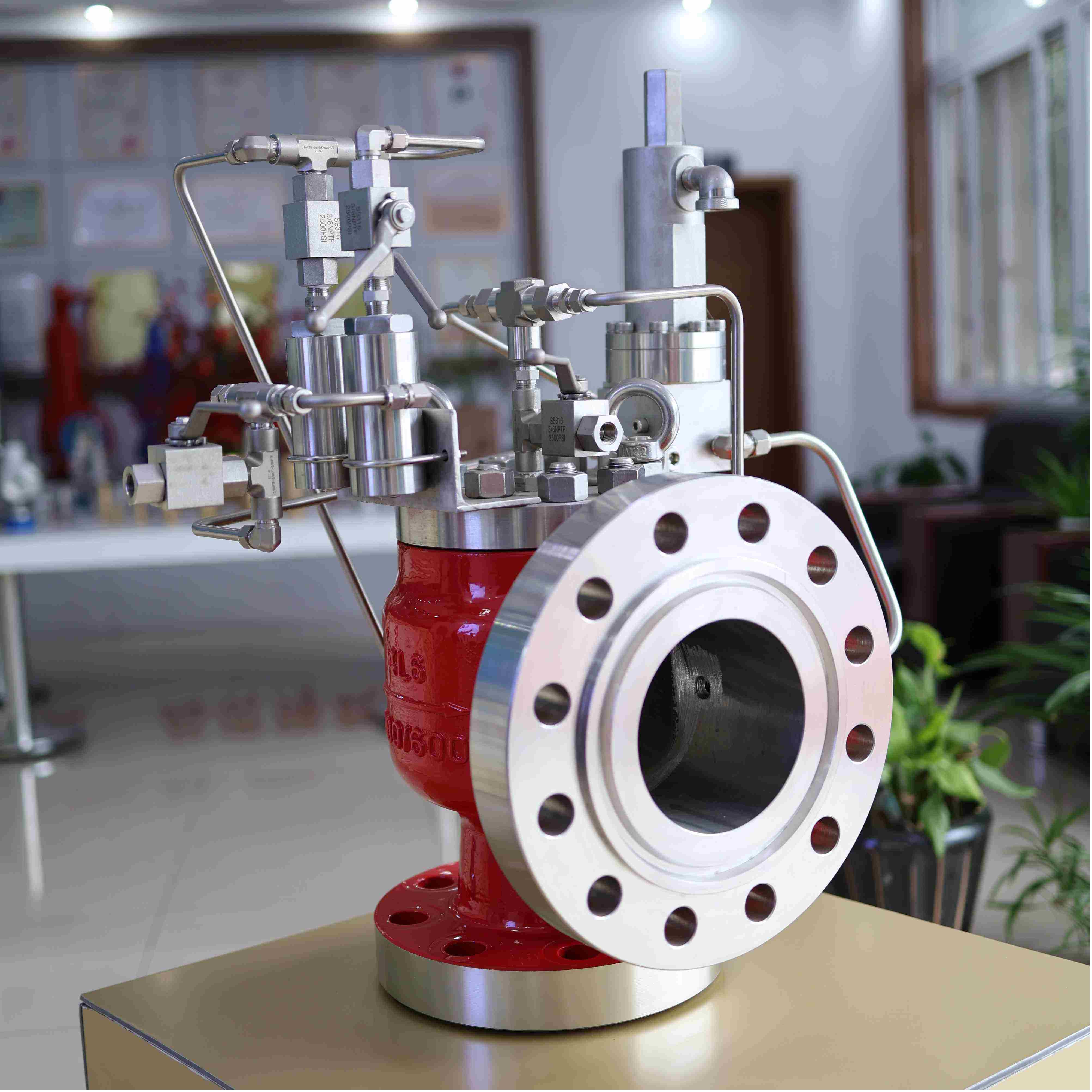
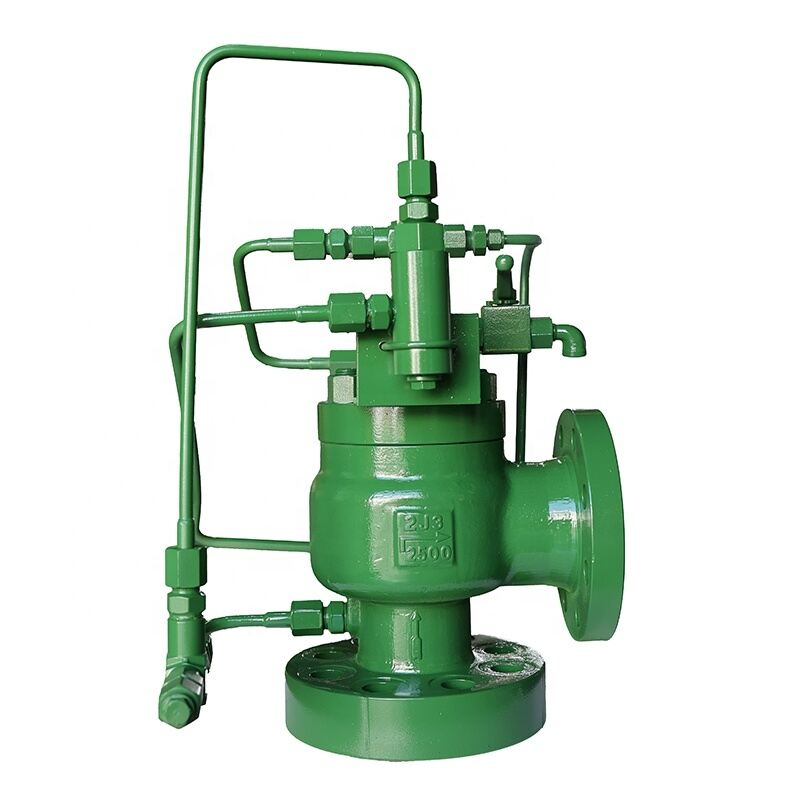


7.Safety Valve for Highly Toxic Media
In conclusion, different types of safety valves are developed to meet the specific requirements of various media and operating conditions, playing an irreplaceable role in industrial safety.
 Hot News
Hot News2026-01-13
2025-11-14
2025-10-20
2025-09-24
2025-09-22
2025-09-19